Workspace
The Workspace in autobotAI offers a cloud-based automation platform powered by an AI engine, enabling users to build and deploy automation bots at scale. With the option to deploy the Workspace on AWS, you maintain control over the AWS account that hosts the Workspace, managing infrastructure, security, and scalability while focusing on automation workflows.
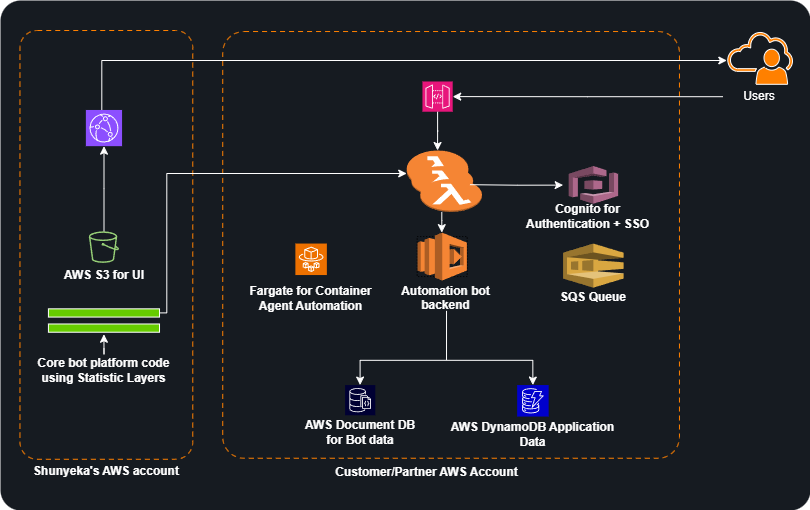
Typical Customer Deployment Overview
When you deploy autobotAI Workspace, the following AWS resources are automatically provisioned in your AWS account:
Compute Resources
- AWS Lambda Functions: Serverless execution engine for automation workflows and API operations
- Amazon ECS Cluster (Fargate): Containerized execution for long-running processes and complex integrations
Data Storage
- Amazon DynamoDB (1 table): Stores workflow metadata, execution history, and user configurations
- Amazon DocumentDB (2 collections): Stores bot definitions, integration configurations, and audit logs
Networking
- Amazon VPC: Private isolated network environment for all workspace resources
- Private Subnets: Host compute and database resources securely
- Public Subnets: Host Application Load Balancer and NAT Gateway
- Internet Gateway: Provides internet connectivity
- NAT Gateway: Enables outbound internet access from private subnets
- Elastic IP: Static IP address assigned to NAT Gateway
- Security Groups: Control inbound and outbound traffic for each service tier
- Network ACLs: Additional subnet-level security controls
API and Authentication
- Amazon API Gateway: RESTful API endpoint for all workspace operations
- Amazon Cognito User Pools: User authentication and authorization
- Amazon Cognito Identity Pools: Federated identity management for AWS service access
Security and Access Control
- IAM Roles: Lambda execution role, ECS task role, API Gateway execution role
- Custom IAM Policies: Least-privilege access policies for each service component
Monitoring and Logging
- Amazon CloudWatch Events: Scheduled automation triggers
- Amazon CloudWatch Logs: Centralized logging for all services
- Amazon CloudWatch Metrics: Performance monitoring and alerting
Note: All resources are deployed within your AWS account. You maintain complete control and ownership of all data and infrastructure.
Architecture: Customer-hosted in your AWS account
Control: Full control over infrastructure, data, and configurations
Availability: Multi-AZ deployment for high availability within a single AWS region
Key Characteristics:
- All resources deployed in customer's AWS account as serverless application.
- Data residency maintained within selected AWS region
- Private VPC deployment with customer-managed networking
- Supports AWS regions:
us-east-1,ap-south-1(additional regions coming soon) - Automatic failover across Availability Zones within the region
- Suitable for organizations requiring full infrastructure control and data sovereignty
Note: For Self-hosted autobotAI workspace, Cross-region deployment and disaster recovery capabilities are available for Workspace deployments with Enterprise support.
Important: For Self-hosted autobotAI workspace, Multi-region active-active deployment is not currently supported. Cross-region replication is available for disaster recovery purposes only.
Key AWS-Related Features of Workspace
-
Scalability: Workspace on AWS enables users to build scalable services that can adjust based on the size and complexity of automation workloads. Users can customize compute and networking configurations for tailored performance.
-
AWS Cognito Integration: Integrate with AWS Cognito to authenticate users via built-in accounts or Single Sign-On (SSO), ensuring secure and efficient user management for automation engineers.
-
AWS ECS & Lambda Integration: Workspace utilizes AWS ECS and AWS Lambda to run automation workflows, allowing users to leverage powerful serverless compute capabilities in a collaborative, low-code environment.
-
AWS API Gateway Integration: API Gateway connects the serverless components of Workspace with the frontend, providing AWS-native security and availability controls for seamless automation service interactions.
-
AWS DynamoDB & DocumentDB: Workspace uses NoSQL databases, such as DynamoDB and DocumentDB, to store metadata and bot-related data within a private VPC. This setup ensures data ownership and control, with data securely stored within your AWS environment.
-
Security and Compliance: Workspace on AWS includes role-based access control, encryption, and compliance with standards such as HIPAA and GDPR. Additionally, AWS security features, such as IAM and VPC, further secure automation workflows.
Resource Sizing and Scalability
Serverless Auto-Scaling
autobotAI leverages AWS serverless services to dynamically scale compute and storage resources, minimizing the need for manual capacity planning.
| Service | Sizing Model | Default Capacity / Range | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| AWS Lambda | Auto-scaling based on demand | 1 GB memory, <1,000 concurrent executions | Memory automatically adjusts per workload |
| Amazon ECS (Fargate) | Auto-scaling based on CPU and memory utilization | 0.25 - 4 vCPU, 0.5 - 350 GB RAM | Scales task count based on policy |
| Amazon DynamoDB | On-demand or provisioned capacity mode | Automatically scales read/write units | Supports burst capacity |
| Amazon DocumentDB | Fixed instance size, scalable storage | Default: 2 x r5.large instances | Enterprise can customize instance size |
Default Configuration
- No manual intervention needed for typical usage.
- Workloads automatically sized for performance and cost.
- Enterprise customers may request reserved capacity for predictable workloads.
Custom Sizing (Enterprise)
For large-scale deployments, custom sizing options include:
- Reserved read/write capacity for DynamoDB
- Dedicated ECS cluster sizing and task limits
- DocumentDB instance type and cluster scaling
- Custom VPC CIDR ranges and subnet sizes
Note: Performance monitoring dashboards provide real-time capacity metrics to aid scaling decisions.
AWS Services Utilized by Workspace
- Lambda Functions
- ECS Cluster (Fargate-based)
- DynamoDB (1 instance)
- DocumentDB (2 tables)
- AWS VPC, Subnets, Elastic IP, and Internet Gateway
- API Gateway (for secure frontend connection)
- Cognito User Pools and Cognito Identity Pools
- IAM Roles and Custom Policies
- CloudWatch Events (for scheduled automation)
- CloudWatch Logs (for monitoring and logging)
Security Best Practices
Principle of Least Privilege
To minimize security risks, follow these least privilege best practices:
-
Initial Deployment Permissions
- Customer can choose to update an IAM user permissions applied with default settings during initial deployment.
- After deployment, remove
AdministratorAccessand assign users the minimum permissions required for daily operations.
-
Service-Specific IAM Roles
autobotAI automatically creates and attaches the following roles with narrowly scoped permissions:- Lambda Execution Role: Access only to specific DynamoDB tables and CloudWatch Logs
- ECS Fargate Execution Role: Permissions to pull container images from ECR and log to CloudWatch
- API Gateway Role: Permission to invoke designated Lambda functions
-
Custom IAM Policies
- Review the auto-generated IAM policies in your AWS console.
- Add inline comments or descriptions to each policy explaining its purpose.
- Use AWS Managed Policies sparingly; prefer custom policies scoped to only necessary actions and resources.
-
Ongoing Access Review
- Conduct quarterly IAM role and policy reviews in IAM Access Analyzer.
- Revoke unused roles and policies.
- Enable AWS CloudTrail to audit API calls for sensitive operations.
Note: Detailed IAM policy JSON examples are available in the Security Best Practices section of our documentation.
Encryption Keys – Purpose and Location
autobotAI uses AWS Key Management Service (KMS) keys to secure data at rest. The following keys are created:
| Key Name | Purpose | AWS Service Used | Location (Region) |
|---|---|---|---|
autobotAI-DynamoDB-Key | Encrypts DynamoDB table data at rest | DynamoDB SSE-KMS | Same as deployment region |
autobotAI-DocumentDB-Key | Encrypts Amazon DocumentDB storage at rest | DocumentDB KMS (Optional) | Same as deployment region |
autobotAI-CloudWatch-Logs | Encrypts CloudWatch Logs groups and log streams | CloudWatch SSE-KMS | Same as deployment region |
autobotAI-Backup-Storage | Encrypts S3 bucket for bot import/export backups | S3 SSE-KMS | Same as deployment region |
Note:
- Customer-managed KMS keys are optional and can be configured with enterprise support.
- Key rotation is enabled annually for AWS-managed keys.
- For higher compliance, you can configure custom key rotation schedules in the KMS console with enterprise support.
- All key usage events are logged in AWS CloudTrail for auditing.
Sensitive Data Storage and Encryption at rest
All customer data is stored within your AWS account in secure, private resources:
| Data Category | Storage Service | Storage Location (Subnet) | Encryption |
|---|---|---|---|
| Workflow Metadata | Amazon DynamoDB | Private Subnets in VPC | SSE-KMS (AWS Default) |
| Bot Definitions & Config | Amazon DocumentDB | Private Subnets in VPC | SSE-KMS (AWS Default) |
| autobotAI Logs | Amazon CloudWatch Logs | Private endpoint | SSE-KMS (AWS Default) |
| Integration Credentials | AWS Secrets Manager | Private endpoint | SSE-KMS (AWS Default) |
| Audit Trails | AWS CloudTrail | S3 (private bucket) | SSE-KMS (AWS Default) |
Note:
- All data is encrypted at rest either using AWS managed or customer-managed keys.
- No data leaves your AWS account unless you explicitly configure cross-region replication or data export.
- Access to all data stores is governed by least-privilege IAM roles and policies.
Encryption in Transit
| Communication Path | Protocol | Certificate/Key Management |
|---|---|---|
| User ↔ API Gateway | TLS 1.2+ | AWS Certificate Manager (ACM) |
| API Gateway ↔ Lambda / ECS | HTTPS | AWS internal TLS |
| Lambda / ECS ↔ DynamoDB / DocumentDB | TLS | AWS SDK encrypted connections |
Note: All public endpoints enforce HTTPS-only access. HTTP traffic is redirected to HTTPS.
Disk and Volume Encryption
Although autobotAI uses serverless services (Lambda, Fargate) with managed storage, any attached EBS volumes (if used for custom tasks) should be encrypted:
Network Configuration
autobotAI Workspace is deployed in a dedicated VPC with public and private subnets, employing security groups and network ACLs for layered security.
VPC and Subnets
- VPC CIDR Block:
10.0.0.0/16(customizable for Enterprise customers) - Public Subnets (2 AZs):
10.0.1.0/24in AZ A10.0.2.0/24in AZ B
- Private Subnets (2 AZs):
10.0.10.0/24in AZ A10.0.20.0/24in AZ B
- Database Subnets (2 AZs):
10.0.30.0/24in AZ A10.0.40.0/24in AZ B
Note: Above mentioned subnets are default subnets from automated deployment cloudformation, Customer has option to choose different CIDR range during workspace deployment.
Internet Gateway and NAT Gateway
- Internet Gateway: Attached to the VPC for public subnet egress/ingress
- NAT Gateway: Deployed in each public subnet, with Elastic IPs for outbound internet access from private subnets
Route Tables
| Route Table | Associated Subnets | Routes |
|---|---|---|
| Public-RT | Public subnets | 0.0.0.0/0 → Internet Gateway |
| Private-RT | Private subnets | 0.0.0.0/0 → NAT Gateway |
| Database-RT | Database subnets | 10.0.0.0/16 → local (no internet) |
Security Groups
| Security Group Name | Purpose | Ingress Rules | Egress Rules |
|---|---|---|---|
autobotAI-ALB-SG | API Gateway / ALB | TCP 443 from 0.0.0.0/0 | All outbound |
autobotAI-App-SG | Lambda & ECS tasks | TCP 443 from autobotAI-ALB-SG | TCP 443 to Database-SG |
autobotAI-Database-SG | DynamoDB, DocumentDB (private) | TCP 443 from autobotAI-App-SG | None |
Note: Security groups follow the principle of least privilege. Do not open additional ports without security review.
Network ACLs
- Public NACL: Allows inbound 80/443, all outbound
- Private NACL: Allows outbound 80/443, ephemeral port range 1024–65535 inbound
- Stateless Rules: Explicit DENY for all other traffic
Caution: Network ACLs are stateless; ensure both inbound and outbound rules are configured appropriately.
Network ACLs
- Public NACL: Allows inbound 80/443, all outbound
- Private NACL: Allows outbound 80/443, ephemeral port range 1024–65535 inbound
- Stateless Rules: Explicit DENY for all other traffic
Caution: Network ACLs are stateless; ensure both inbound and outbound rules are configured appropriately.
Costs and Billing Overview
Below is a list of AWS services used by autobotAI Workspace, with guidance on which are core (mandatory) and which are optional based on feature usage.
| AWS Service | Usage Purpose | Billing Model | Mandatory? | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AWS Lambda | Execution of automation workflows | Per request + duration | Yes | Core compute layer |
| Amazon ECS (Fargate) | Long-running integrations | vCPU and memory usage | Yes | Core compute for container workflows |
| Amazon DynamoDB | Metadata, configs, execution history | On-demand or provisioned capacity | Yes | Core data store |
| Amazon DocumentDB | Bot definitions and audit logs | Instance hours + storage | Yes | Core data store |
| Amazon API Gateway | Exposes RESTful APIs | Per million requests + data transfer | Yes | Core API interface |
| Amazon Cognito | User authentication and identity management | MAUs (monthly active users) | Yes | Core authentication |
| Amazon S3 | Bot import/export storage | Per GB stored + request fees | Optional | Only if using import/export functionality |
| AWS Key Management Service (KMS) | Encryption at rest | Per key per month + API calls | Optional | Additional compliance/encryption costs |
| Amazon CloudWatch | Logs and metrics storage | Per GB ingested + custom metrics | Yes | Core monitoring |
| Amazon CloudTrail | API call audit logging | Per GB delivered to S3 | Optional | Recommended for compliance, can archive externally |
| Amazon Bedrock | Inferance tokens | Per API call and inferance token | Optional | Recommended for agentic secops workflow |
Note:
- For exact pricing, refer to the AWS Pricing Calculator and your AWS Marketplace subscription details.
- Enterprise customers may negotiate reserved capacity for DynamoDB or Lambda Provisioned Concurrency for cost savings.
Software Upgrades and Patch Management
autobotAI operates on a fully serverless AWS infrastructure, leveraging AWS managed services for compute, storage, and networking. Consequently, manual system-level patching or hardening is not required.
Workspace Version Upgrades
- autobotAI releases new workspace versions periodically, containing backend code, runtime updates, container images, and database schema changes if necessary.
- Customers initiate workspace upgrades via the autobotAI portal, selecting the desired version.
- The upgrade process includes automated deployment of new AWS Lambda functions, ECS Fargate tasks, and database migrations.
- autobotAI manages version rollbacks and staged rollouts internally to ensure stability.
Note: Customers should monitor upgrade notifications and plan workspace version upgrades during planned maintenance windows to minimize workflow disruption.
Workspace Health Monitoring
Workspace health can be effectively monitored through the following methods:
1. autobotAI Activity Notification
- The workspace provides an Activity Tab that tracks bot execution events, success/failure rates, and operational anomalies.
- Monitor workflow execution outcomes in near real-time to identify failed runs or workflow bottlenecks.
- Configurable alerting mechanisms allow email or webhook notifications on critical failure events.
2. AWS Native Logs and Metrics
- Amazon CloudWatch Logs capture detailed logs for Lambda functions, ECS tasks, and API Gateway.
- Key CloudWatch metrics include:
- Lambda invocation count, duration, error rate
- ECS CPU and memory utilization
- DynamoDB read/write capacity and throttling
- API Gateway request count, latency, and errors
Monitoring these metrics provides insight into the operational health of autobotAI components and identifies potential infrastructure or integration issues.
Note:
Combining autobotAI's activity monitoring with AWS CloudWatch metrics delivers a comprehensive view of system health and performance, enabling prompt detection and response.
